译者 王为
文中黑字部分为原文,蓝字部分为译文,红字部分为译者注释或补充说明
US Inflation comment: Still flying high
by Anders Svendsen

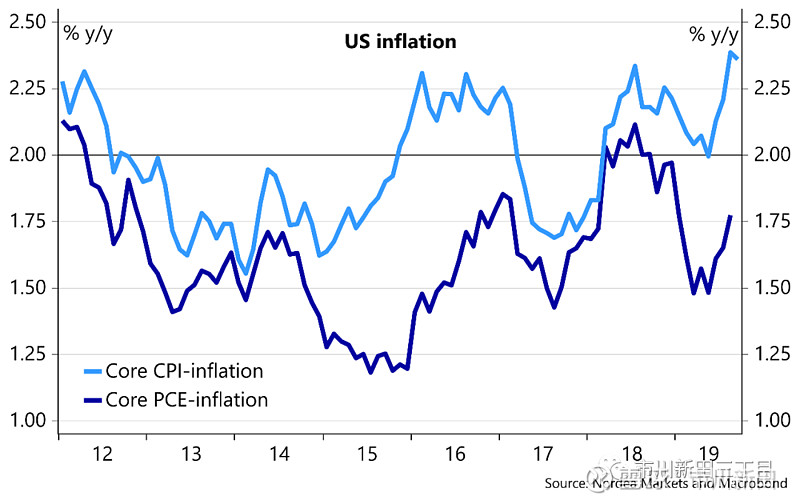
Core CPI inflation remains at the highest inmore than 10-years despite cooling momentum.
尽管增长动能有所放缓,但美国核心消费物价指数仍处于10多年来的最高位
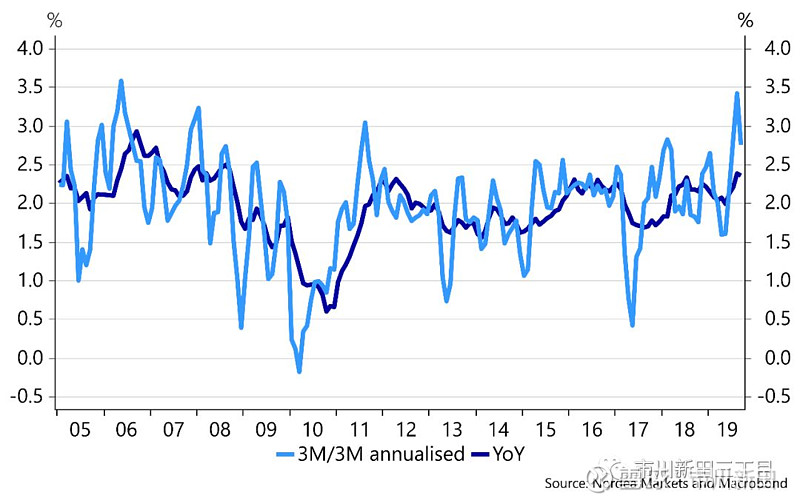
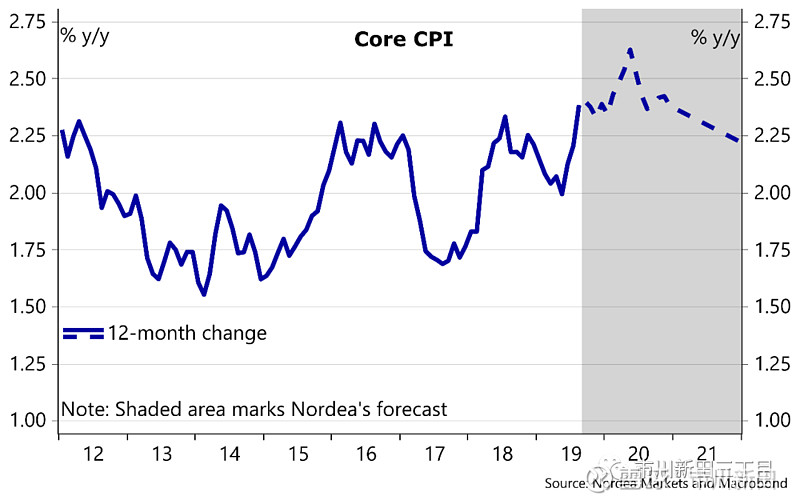
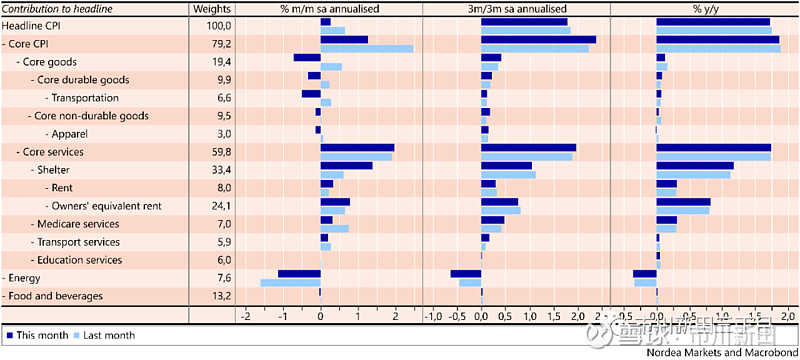
Core CPI: 0.1% m/m (Nordea: 0.2%, Consensus: 0.2%, previous: 0.3%), corresponding to unchanged core CPI inflation at 2.4%.
核心消费物价指数:月度环比增速为0.1%,北欧联合银行的预测值为0.2%,市场预测值为0.2%,前值为0.3%,所对应的年度同比增速保持不变,仍维持在2.4%;
CPI YoY: 1.7% (August: 1.7%)
消费物价指数的年度同比增速为1.7%;
Headline CPI: 0.0% m/m (Consensus: 0.1%, previous: 0.1%), corresponding to unchanged headline CPI inflation at 1.7% y/y.
名义消费物价指数:月度环比增速为0.0%,市场预测值为0.1%,前值为0.1%,所对应的年度同比增速保持不变,仍为1.7%。
Core CPI increased slightly less than expected in September, while remaining unchanged at 2.4% y/y. The main culprits of the weaker-than-expected momentum in core CPI was a 1.6% drop in used-car prices during September, while new vehicle costs were down 0.1% and apparel prices fell 0.4%. Headline CPI also increased slightly less than expected and headline CPI inflation is trending lower due to decreasing energy prices.
9月份核心消费物价指数的月度环比增速略低于市场预期,与去年同期相比增速仍保持在2.4%。核心消费物价指数的增长动能之所以会低于预期主要原因在于9月份二手车的成交价出现了幅度为1.6%的下跌,而新车价格下跌了0.1%,服装价格下跌了0.4%。名义消费物价指数的增速也略低于预期,主要是受到能源价格下跌的影响。
Goods prices are on the rise
商品的价格出现上涨
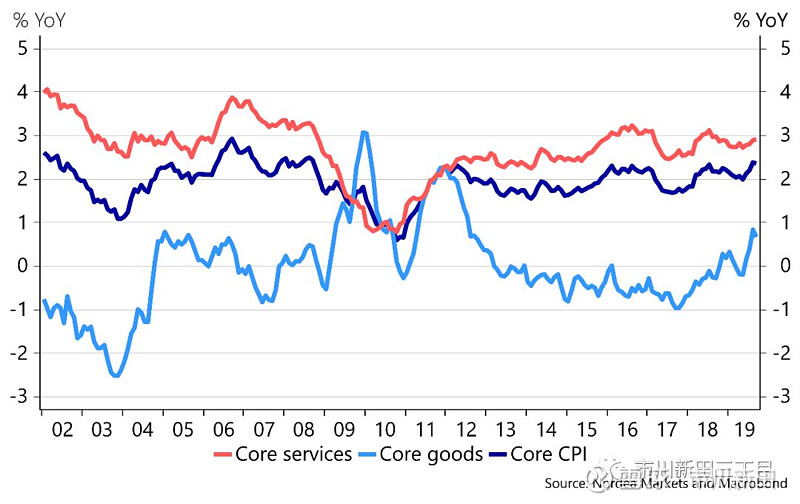
Core CPI has been above or at 2% since March-2018, to a large extent driven by growth in core services prices. However, over the last months core goods prices have clearly increased and now stand close to the highest level since 2012 in year-over-year terms.
2018年3月以来,核心消费物价指数的年化同比涨幅从未低于过2.0%,很大程度上是受核心服务业物价上涨的推动。但在过去几个月里,核心商品的价格出现了明显地上涨,如今年化同比涨幅已接近2012年以来的最高点。
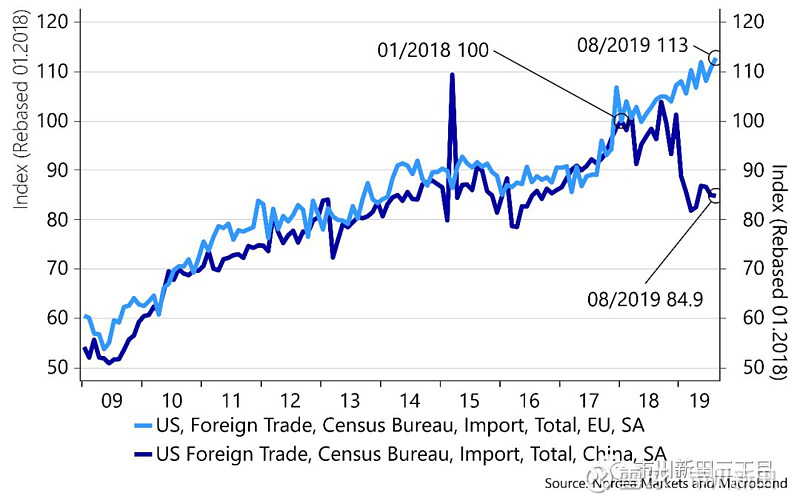
Core goods inflation has been structurally low for more than two decades; however, implementation of tariffs has started to become somewhat visible, especially for Photographic equipment, Education and Apparel. Up until now, US consumers have been vastly shielded from higher US tariffs on imported Chinese goods due to a stronger USD. Moreover, tariffs have mainly hit intermediary goods bought by firms and import streams have to some degree been redirected from China to Vietnam and the EU for instance. Figures from the US Census Bureau indicate that Chinese imports were down approximately 15% from the beginning of 2018 until August 2019 whereas imports from the EU during the same period were 13% higher (see the chart below).
核心商品价格在过去二十多年里处于结构性的低增长状态,但是加征关税带来的后果开始显现出来,摄影器材的价格、教育开支和服装的价格受到的影响尤其明显。美国对中国进口商品加征关税的负面影响直到如今尚未明显波及到美国消费者的原因是因为美元汇率在升值。此外,加征关税影响的主要是企业购买的半成品,有些进口货源也从中国转向了其他国家,比如越南和欧洲。来自美国人口调查局的数据显示,从2018年年初至2019年8月,美国自中国进口货物的总额大约减少了15%,而同期来自欧洲的进口则增加了13%,见下面第三张图。
However, going forward, the US consumer could get used to increasing goods prices for a prolonged period for the first time since 2012-2013. The main culprit is more tariffs. The latest round of tariffs from September on Chinese imported goods also involve consumer goods. Furthermore, more tariffs are due 1 December, unless a postponement or cancellation is agreed in advance.
但是继续下去的话,美国消费者有可能会适应进口商品价格自2012-2012年以来首次出现长期上涨的事实,而导致这一情况发生的原因就是加征关税。9月初以来对中国输美商品最新一轮加征关税也对消费类商品产生了影响。此外从12月1日起,还将有更新一轮加征关税开始生效,除非在此之前达成延迟加税或取消加税的协议。
Moreover, wage growth is still close to the highest level since 2009. Therefore, service prices could continue to grow around their current rates. Given these factors, we see some inflationary risks over the next quarters.
除此之外,薪酬水平的增速仍接近2009年以来的最高位。因此,服务业的物价增速有可能维持在现有水平附近。考虑到这些因素,我们认为在未来几个季度里通胀增速有一些加速的可能性。
Higher core inflation will not prevent Fed cuts
核心通胀增速处于高位不会令联储停止降息
Stronger inflationary pressure has also started to appear in Fed’s favourite inflation measure, Core PCE, which hit 1.8% y/y in August. Even if Core PCE converges towards the 2% target over the next months, we don’t expect it to have much implication for monetary policy. Fed has earlier indicated that they would like to see inflation above 2 % for a prolonged period to be in line with its symmetrical 2% target.
通胀压力增加的迹象也开始出现在联储最喜欢使用的通胀指标——个人消费开支物价增速的核心值上,其8月份的年化同比增速为1.8%。即使个人消费开支物价增速的核心值在未来几个月里靠近联储设定的2%的目标值,我们也不认为这将对联储的货币政策产生多大影响。联储先前表示希望见到通胀率长期处于2%以上,这样就会与联储设定的2%的目标值保持一致。
More importantly is the contraction among US manufacturers and weaker growth among US non-manufacturers. Therefore, we expect another 25bp rate cut in both October and December with risks tilted towards another cut in 2020.
更重要的是近期美国制造业活动出现收缩同时美国非制造业增速乏力,因此,我们预测联储会在10月份和12月份的例会上分别降息25个基点,2020年也有一次降息的可能性。