4. Industry Overview
4.1 Market Size
The global luxury market reached new heights in estimates, which suggests it hit a record value of €1.5 trillion (USD 1.63 trillion) in 2023. This represents an impressive growth of 8% to 10% compared to 2022. It is estimated to reach a CAGR of 3.22% between 2024 and 2028, while its market size is forecasted to reach USD 392.40 billion by 2030. This signifies growth from USD 272.74 billion in 2022. Fueled by a surge in demand from affluent millennials and Gen Z, the luxury sector is booming. Four key trends drive this growth: the digital transformation of the luxury world, the rise of luxury consumption in emerging markets, a growing appreciation for quality and sustainable fashion, and a shift in what defines luxury for younger generations.
4.2 Growth Drivers
4.2.1 Digital Transformation
Moreover, studies have predicted that online will soon surpass all other luxury sales channels, signifying a profound shift in consumer behavior and market dynamics. This transformation is driven by the growing preference for the convenience and accessibility of online shopping, especially among digital natives like Millennials and Gen Z, who value the seamless experiences offered by e-commerce. Advanced e-commerce platforms now provide sophisticated user experiences with high-resolution product images, detailed descriptions, and secure transactions, enhancing consumer trust and satisfaction. For instance, according to some research, the share of online sales for personal luxury goods will grow to 33% by 2033 (Figure 3). This shows how important enhancing the digital presence will be for luxury brands in the future.
Technologies such as augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) bridge the gap between online and offline shopping, offering immersive experiences. AI-driven recommendation engines personalize shopping by analyzing consumer behavior. This technological transformation aims to create a more unique and enjoyable shopping experience.
Luxury brands leverage data analytics and social media for targeted advertising and influencer collaborations to reach and engage wider audiences. The direct-to-consumer (DTC) model eliminates intermediaries and allows brands to control pricing and customer experience while offering exclusive online collections. E-commerce also facilitates global market reach, enabling brands to enter emerging markets and tailor strategies to local preferences. The wealth of data from online sales empowers brands to make informed decisions and improve customer satisfaction, highlighting the significant impact of digital transformation in driving growth for the luxury industry.
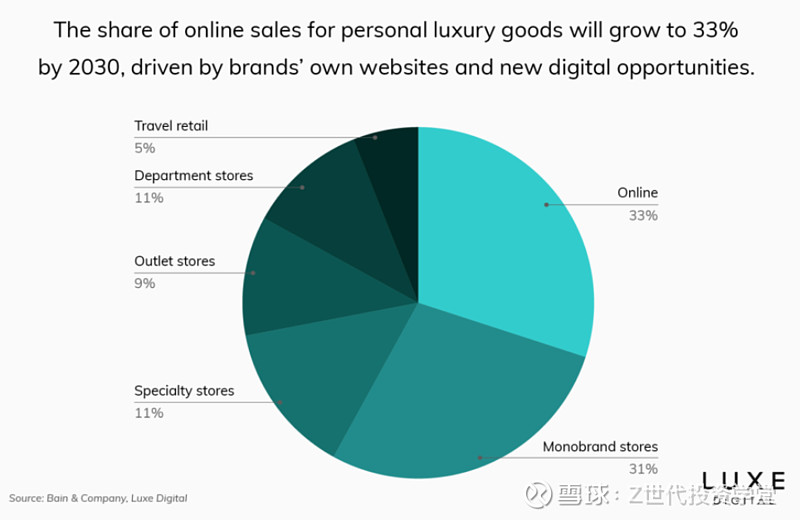
Figure 3
4.2.2 A New Era of Consumers
In addition, the rise of Millennials and Generation Z as dominant consumer demographics significantly drives growth in the luxury industry. These cohorts, born between the early 1980s and the early 2010s, bring unique preferences and behaviors that reshape the luxury market. For instance, Millennials and Gen Z accounted for the entire growth of the global luxury market in 2022, according to Bain and Altagamma’s study. Indeed, both Millennials and Gen Z have grown up in a digital era, making them adept at online shopping and digital interactions. They prefer shopping on mobile devices and value the convenience and accessibility of e-commerce platforms. Luxury brands that invest in sophisticated online presences and mobile-optimized websites are better positioned to capture the attention of these tech-savvy consumers.
Similarly, social media plays a crucial role in the purchasing decisions of millennials and Gen Z. Platforms like Instagram, TikTok, and Snapchat are integral to their lives as they follow influencers, celebrities, and brands. Luxury brands that effectively leverage social media marketing collaborate with influencers, and create engaging and authentic content can build strong connections with these demographics. As a result, it is estimated that Gen Z and Alpha affluent consumers will make up 30% of the luxury market by 2030, growing three times faster than other generations (Figure 4).
Therefore, another important topic to discuss in the coming years is the next generation of ‘Alpha affluent consumers.’ One example of such consumers is Chinese consumers. They are still expected to drive a significant increase in luxury spending, projected to account for 40% of the global luxury market by 2030, down from the previously forecasted 50% by 2025, as reported by Bain & Co. Furthermore, other Asian countries, such as India and Indonesia, are witnessing a rise in wealth among their consumers. This shift is evident in luxury brands' strategies, such as Louis Vuitton appointing actress Deepika Padukone as its first Indian "House Ambassador" in May 2022, highlighting the brand's focus on the Indian market.
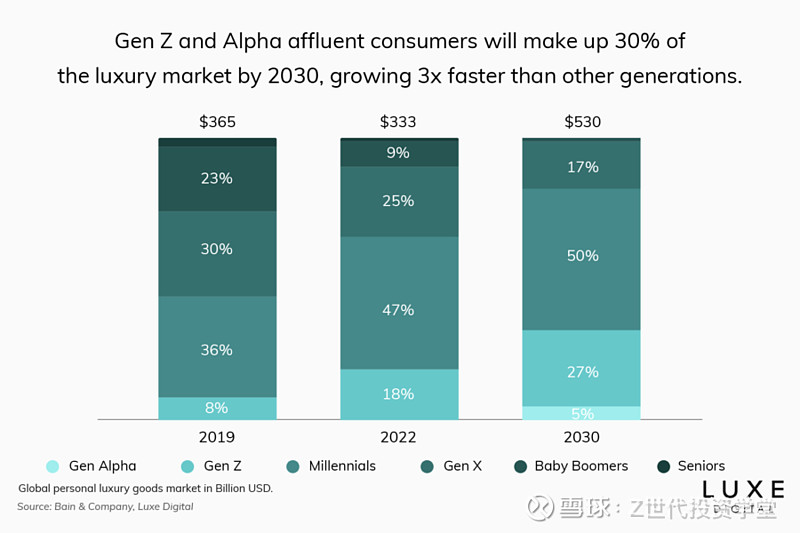
Figure 4
4.2.3 Sustainability and Second-hand Market Boom
Luxury goods companies have rebounded to pre-pandemic profitability levels and are also undergoing a significant transformation towards an environmentally responsible, circular economy business model. This shift is driven by customer demand and increasing regulatory pressure, and technology is crucial in accelerating this green transition.
Indeed, consumer demand for ethical practices is rising, especially among Millennials and Gen Z, who are increasingly prioritizing sustainability. They expect brands to demonstrate a genuine commitment to ethical practices, including environmentally friendly production methods, fair labor practices, and responsible materials sourcing. Hence, luxury brands are responding by adopting sustainable practices, such as using recycled materials, reducing carbon footprints, and ensuring transparency in their supply chains. For example, brands like Stella McCartney and Gucci have been at the forefront of sustainable luxury, integrating eco-friendly materials and processes into their products.
Moreover, in recent years, there has been a boom in the second-hand luxury market. Indeed, the rise of online resale platforms such as The RealReal, Vestiaire Collective, and Poshmark has facilitated the growth of the second-hand luxury market. These platforms offer a wide range of authenticated luxury items, providing consumers with a trustworthy and convenient way to purchase and sell pre-owned luxury goods. According to a report by Bain & Company, the second-hand luxury market is growing four times faster than the primary luxury market. This trend is expected to continue, with more consumers embracing the circular economy and the concept of e-commerce. In reaction to this trend, many luxury brands are now entering the second-hand market. For instance, Gucci has partnered with The RealReal to offer pre-owned items, and Burberry has launched its own resale platform. These initiatives allow brands to maintain control over their products’ secondary lifecycle and reinforce their commitment to sustainability.
Therefore, by participating in the second-hand market, brands can reach a broader audience, including younger consumers more inclined towards sustainable consumption practices. These brands can build stronger relationships with their consumers as ethical and sustainable practices resonate well with modern consumers, fostering brand loyalty and encouraging repeat purchases. They can also help make high-end goods accessible to a wider audience. This democratization of luxury can drive growth by tapping into new customer segments who value quality but are also price-sensitive and eco-conscious.
4.2.4 Focus on Personalization
Personalization is a powerful growth driver for the luxury industry, significantly transforming how brands engage with their consumers and enhancing the overall customer experience. Modern luxury consumers, particularly Millennials and Gen Z, seek unique, personalized products that reflect their individual tastes and preferences. Brands are responding by offering bespoke services, such as custom-made clothing and tailored beauty products while creating personalized shopping experiences through advanced technologies like AI and data analytics. These technologies allow brands to understand consumer preferences and deliver tailored recommendations, enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty. Augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) further revolutionize the shopping experience by allowing customers to try on products and explore customized designs virtually.
Moreover, effective personalized communication, through targeted messaging and content and personalized loyalty programs, fosters strong customer relationships and loyalty. Additionally, personalization allows luxury brands to cater to diverse markets and broaden their reach by tailoring offerings to meet the specific preferences of different consumer segments. This focus on personalization enhances the customer experience, drives innovation, and supports sustainable growth in the competitive luxury market.
Figure 5 clearly illustrates the key elements defining the 'new' luxury paradigm.
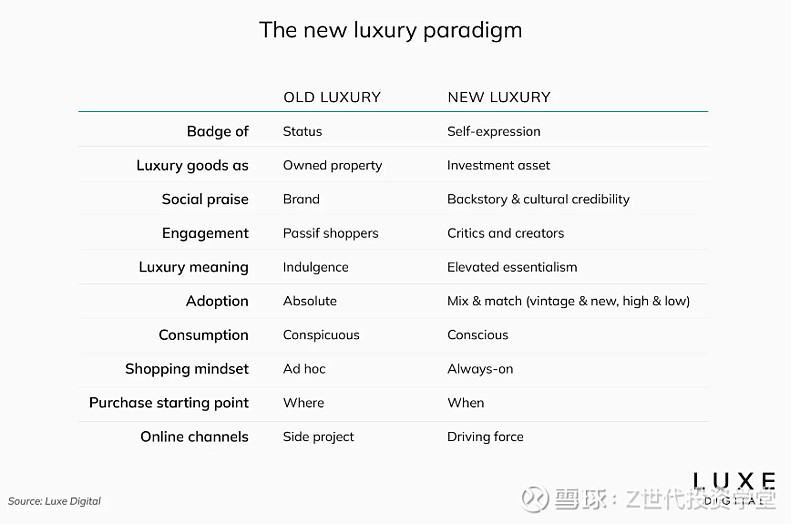
Figure 5
4.3 Competitor Analysis
The competitor analysis provides a deeper insight into LVMH’s competitive landscape and overall market positioning relative to other key players in the industry. The following section compares LVMH with its main competitors, highlighting selected ratios and performance metrics to illustrate their relative strengths and weaknesses.
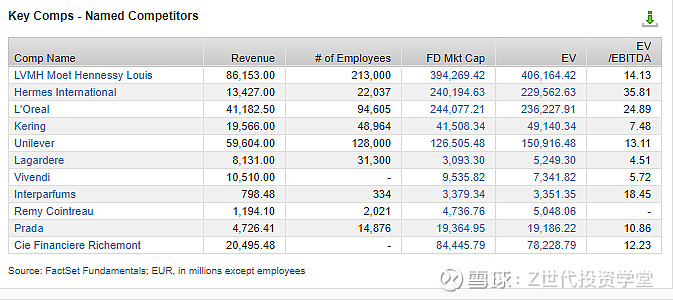
Figure 6
4.3.1 Market Capitalization
Figure 6 illustrates a compelling observation regarding the market capitalizations of top competitors within the luxury goods sector. Notably, LVMH stands out prominently with the highest market capitalization recorded at €394.2 million. This figure underscores LVMH's formidable position within the industry, reflecting its robust financial performance, strong brand portfolio, and strategic market positioning.
LVMH's substantial market capitalization signifies its dominant presence in the luxury market and underscores investor confidence in the company's ability to generate sustainable growth and deliver value over the long term. This significant valuation places LVMH at the forefront of its peers, highlighting its resilience and adaptability in navigating dynamic market conditions and evolving consumer preferences.
Moreover, LVMH's commanding market capitalization speaks to its competitive advantage and strategic initiatives to drive innovation, expand into new markets, and nurture its luxury brand ecosystem. By consistently delivering exceptional products and experiences while staying true to its heritage and commitment to excellence, LVMH continues to solidify its position as a global leader in the luxury goods industry, setting a benchmark for its competitors to aspire to.
4.3.2 Revenues
In terms of revenue generation, LVMH once again demonstrates its industry dominance with a total revenue of €86.153 million. This impressive figure underscores the group's robust business model and ability to leverage a diverse portfolio of luxury brands across various sectors, including fashion, leather goods, perfumes, cosmetics, watches, jewelry, wines, and spirits.
LVMH's ability to consistently deliver high revenue also reflects its successful execution of targeted acquisitions and organic growth strategies. By integrating new and complementary brands into its portfolio while preserving their unique identities and autonomy, LVMH has enhanced its market reach and strengthened its competitive edge.
Furthermore, the group's emphasis on digital transformation and enhancing the customer experience through cutting-edge technologies has played a crucial role in driving sales and revenue. By optimizing its value chain and ensuring seamless integration from product conception to distribution, LVMH has maximized operational efficiencies and met the evolving demands of a discerning global clientele.
4.3.4 Enterprise Value (EV)
Furthermore, LVMH’s enterprise value (EV) stands out significantly, surpassing all its competitors by a substantial margin. With an EV of €406,164 million, LVMH's valuation is nearly double that of Hermès, triple that of Unilever, and quadruple that of Richemont. This exceptional enterprise value not only underscores LVMH's financial strength but also highlights its absolute dominance within the luxury goods sector.
The remarkable EV of LVMH reflects the market's confidence in the company's future growth prospects and its ability to generate substantial cash flows. It indicates a high level of investor trust in LVMH's strategic direction, management capabilities, and overall market positioning. This high valuation is a testament to the group's successful execution of its long-term vision, which includes a focus on innovation, brand diversification, and sustainable development.
In summary, LVMH’s enterprise value highlights its commanding position in the luxury goods sector and showcases its strategic prowess and ability to deliver exceptional value to shareholders. This dominance in EV is a clear indicator of LVMH's robust market standing and its potential for continued success and expansion in the future.
4.3.4 P/E and EV/EBITDA Ratio
Lastly, LVMH has an EV/EBITDA ratio of 14.13, which positions it competitively among its peers. To provide context, this ratio is a key financial metric used to assess a company's valuation. It compares the enterprise value (EV) to the earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA), offering insights into a company's overall financial health and valuation efficiency.
For LVMH, an EV/EBITDA ratio of 14.13 suggests that investors are willing to pay 14.13 times the company's EBITDA for its enterprise value. When compared to its competitors, this figure provides a benchmark for evaluating LVMH's market valuation relative to its earnings:
Hermès: With an EV/EBITDA of 35.81, Hermès is valued much higher relative to its EBITDA. This indicates that investors see Hermès as having a very strong earnings potential or lower risk, justifying a higher multiple.
L’Oréal: At 24.89, L’Oréal's ratio is also significantly higher than LVMH's, suggesting that the market perceives L’Oréal's earnings potential or stability as superior to LVMH's.
Kering: Kering's ratio of 7.48 is notably lower, indicating that the market might view Kering as having a higher risk or lower growth potential compared to LVMH.
Prada: Prada’s EV/EBITDA ratio of 10.86 places it below LVMH, suggesting it might be seen as slightly less attractive in terms of growth potential or stability relative to LVMH.
LVMH's EV/EBITDA ratio of 14.13 indicates a balanced perception by investors. It reflects confidence in the company's profitability and growth prospects while considering its risk profile. This ratio, being lower than Hermès and L’Oréal, suggests that LVMH might be undervalued compared to these companies, potentially offering better investment value. Conversely, its higher ratio compared to Kering and Prada underscores LVMH's stronger market position and perceived stability.
In summary, the EV/EBITDA ratio helps investors compare LVMH's valuation efficiency to its competitors, highlighting LVMH's balanced and competitive market standing. This metric provides a snapshot of how LVMH is valued in relation to its earnings, indicating robust investor confidence and a solid financial foundation.
5. Investment Thesis
The investment thesis of LVMH (Louis Vuitton Moët Hennessy) revolves around its position as a global leader in the luxury goods industry and its ability to capitalize on the growing demand for luxury products worldwide. Here are some key aspects of LVMH's investment thesis:
5.1 A Strong Brand Portfolio

Figure 7
LVMH Moët Hennessy Louis Vuitton SE, the world's leading luxury goods conglomerate, presents a compelling investment thesis centered around its unparalleled brand portfolio. This diverse collection spans fashion and leather goods, perfumes and cosmetics, watches and jewelry, wines and spirits, and selective retailing, mitigating risks and capitalizing on various market trends. The portfolio includes iconic brands like Louis Vuitton, Dior, Fendi, Guerlain, TAG Heuer, Moët & Chandon, and Sephora, each maintaining strong identities and deep customer loyalty, which supports premium pricing and market leadership. LVMH leverages synergies across its brands, sharing best practices in design, production, and marketing, while strategic acquisitions, such as Tiffany & Co., bolster its market position. This strength translates into robust financial performance, generating high revenues and profitability and ensuring continuous investment in innovation and expansion. Ultimately, LVMH's diverse and prestigious brand portfolio provides a solid foundation for sustained growth and competitive advantage, making it a highly attractive investment opportunity.
Moreover, LVMH is deploying a strategy focused on diversifying its brands and conquering new markets while remaining true to its heritage and commitment to excellence. By fostering a long-term vision, the group invests in innovation and sustainable development of its Houses, ensuring their growth and adaptability to luxury market trends.
Therefore, the synergy among its various brands enables LVMH to enjoy a unique position in the market, offering various high-end products that cater to the desires of a demanding international clientele. Moreover, LVMH emphasizes strengthening its leadership by integrating digital technologies to enhance the customer experience and optimize its value chain, from design to distribution. This strategic approach is complemented by a targeted acquisition policy to integrate new houses into the LVMH group portfolio while preserving their identity and autonomy, thus stimulating organic growth and accessing new market segments.
5.2 An Emphasis on Product Sustainability
LVMH integrates sustainability as a core component of its investment thesis. The group’s emphasis on sustainable practices not only aligns with growing consumer preferences for eco-conscious brands but also enhances its long-term profitability and resilience.
Circular Economy & Eco-Design Integration
First of all, LVMH actively embraces circular economy principles, aiming to minimize waste and maximize resource efficiency throughout its value chain. By designing products with recyclability and durability in mind, the company extends the lifespan of its luxury goods. Moreover, LVMH explores innovative ways to repurpose materials and components, contributing to a closed-loop system where materials are reused or recycled rather than disposed of. For example, Louis Vuitton launched the ReBelle collection, which features handbags made from upcycled materials sourced from pre-existing LV bags. This initiative extends the lifespan of luxury items and promotes a circular economy model within the brand.
Second-Hand Market Initiatives
Secondly, recognizing the growing popularity of the second-hand luxury market, LVMH strategically engages with this sector. The company supports initiatives that promote the resale and revaluation of pre-owned luxury items, either through its own platforms or in collaboration with reputable partners. By encouraging consumers to buy pre-owned items or participate in resale programs, LVMH extends the lifecycle of its products and reduces the overall environmental footprint associated with luxury consumption. An instance of LVMH's support for the second-hand market is evident in Celine's decision to reintroduce the iconic Phoebe Philo Bag, first launched in the 2010s, to the resale market. Through reintroducing sought-after designs, Celine promotes the purchase of pre-owned items, fostering waste reduction and advancing a more sustainable consumer approach.
Supply Chain Sustainability
LVMH places a strong emphasis on ensuring sustainability across its entire supply chain. This includes responsible sourcing of raw materials, ethical labor practices, and reducing carbon emissions in transportation and logistics. By working closely with suppliers and implementing rigorous standards and certifications, LVMH strives to minimize environmental and social impacts associated with production processes. Additionally, the company invests in technology and innovation to enhance transparency and traceability within its supply chain, allowing for greater visibility into the origins and journey of its products. For instance, Bvlgari implemented an ethical sourcing program for its jewelry, ensuring that diamonds and precious metals are responsibly mined and sourced. By adhering to strict ethical and environmental standards, Bvlgari minimizes the negative impacts of mining operations on local communities and ecosystems.
5.3 Strategic Acquisitions
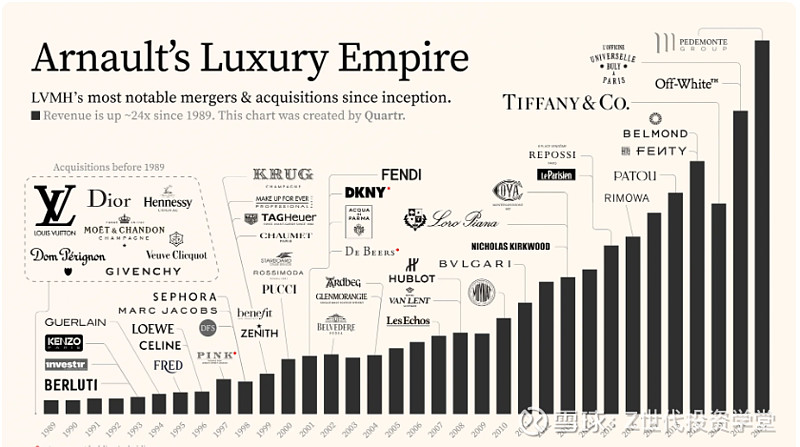
Figure 8
LVMH strategically leverages acquisitions as a key component of its investment thesis. Through targeted acquisitions, LVMH expands its brand portfolio, strengthens its market position, and drives long-term growth and profitability.
Indeed, LVMH strategically acquires luxury brands that complement its existing portfolio or offer strategic synergies. By diversifying its brand portfolio across different sectors, such as fashion, cosmetics, watches, and wines, LVMH mitigates risks and capitalizes on opportunities in various segments of the luxury market. In addition, strategic acquisitions enable LVMH to consolidate its market position and gain a competitive advantage. By acquiring established brands with strong brand equity and market recognition, LVMH enhances its global footprint and captures new customer segments. Acquisitions also provides access to new distribution channels and market segments, enabling LVMH to reach a broader audience and capitalize on emerging market trends.
Moreover, LVMH excels in integrating acquired brands into its business ecosystem while preserving their unique identities and heritage. The group leverages its operational expertise, marketing prowess, and financial resources to unlock synergies and drive value creation. By optimizing supply chains, streamlining operations, and implementing best practices, LVMH enhances the performance and profitability of acquired brands, maximizing return on investment. The group also invests in research and development to enhance product offerings, innovate new designs, and capitalize on emerging consumer trends. Additionally, LVMH leverages the expertise and creativity of acquired brands to drive innovation across its entire portfolio, fostering a culture of excellence and creativity.
Lastly, strategic acquisitions contribute to LVMH's financial performance and shareholder value. By expanding its brand portfolio and market presence, LVMH generates incremental revenue streams and enhances profitability. Furthermore, successful acquisitions strengthen investor confidence and drive shareholder returns, reinforcing LVMH's position as a top-tier investment in the luxury goods sector.
Here are examples of strategic acquisitions made by LVMH:
Tiffany & Co. (2020): LVMH acquired Tiffany & Co., one of the world's most iconic luxury jewelry brands, in a landmark deal valued at $15.8 billion. This acquisition expanded LVMH's presence in the high-end jewelry market and strengthened its position in the United States, while also providing opportunities for synergies and growth in other regions.
Belmond Ltd. (2019): LVMH acquired Belmond Ltd., a global collection of luxury hotels, trains, and river cruises, for $3.2 billion. This acquisition bolstered LVMH's presence in the luxury hospitality sector and complemented its portfolio of prestigious brands, including Louis Vuitton and Moët & Chandon, offering new opportunities for cross-brand collaborations and experiential luxury offerings.
Rimowa (2016): LVMH acquired Rimowa, a leading German luxury luggage manufacturer known for its high-quality aluminum and polycarbonate suitcases, in a deal estimated at €640 million. This acquisition expanded LVMH's presence in the travel and accessories market and provided innovation and brand development opportunities within the luggage category.
Christian Dior (2017): LVMH acquired the remaining shares of Christian Dior that it did not already own, in a deal valued at €12.1 billion. This acquisition consolidated LVMH's control over one of its most iconic fashion brands, providing greater operational flexibility and alignment of strategic objectives within the LVMH group.
Benefit Cosmetics (1999): LVMH acquired Benefit Cosmetics, a San Francisco-based beauty brand known for its quirky packaging and fun-loving approach to makeup, in a deal estimated at $500 million. This acquisition expanded LVMH's presence in the cosmetics industry and provided opportunities for growth in the mass-market beauty segment.
These examples highlight LVMH's strategic approach to acquisitions, which aims to enhance its brand portfolio, strengthen its market position, and drive long-term value creation for shareholders. Through targeted acquisitions, LVMH continues to expand its footprint in key luxury sectors and capitalize on emerging market trends, solidifying its position as a global leader in the luxury goods industry.
5.4 Digital Innovation
Lastly, LVMH prioritizes digital innovation as a core component of its investment thesis. By leveraging cutting-edge technologies and digital platforms, LVMH enhances customer engagement, optimizes operations, and drives long-term growth and profitability.
First of all, LVMH embraces digital transformation within its retail network, integrating online and offline channels to create a cohesive omnichannel experience. Through initiatives like click-and-collect, virtual try-on, and in-store digital activations, LVMH bridges the gap between physical and digital retail, catering to the evolving needs and preferences of modern consumers. Some LVMH brands, such as Bulgari, leverage augmented reality (AR) technology to enable virtual try-on experiences for jewelry and watches. Customers can use their smartphones to visualize how pieces will look on them before making a purchase, enhancing confidence and reducing returns. By investing in technologies like RFID, IoT, and augmented reality, LVMH enhances inventory management, improves operational efficiency, and elevates the overall retail experience. For instance, Sephora offers services like click-and-collect, where customers can order products online and pick them up in-store, blurring the lines between digital and physical retail.
Secondly, digital innovation plays a crucial role in product design and development at LVMH. By leveraging 3D modeling, digital prototyping, and additive manufacturing technologies, LVMH accelerates the product development cycle, reduces time to market, and fosters creativity and innovation. Moreover, digital tools enable LVMH to optimize supply chain management, minimize waste, and enhance sustainability across its brands.
Lastly, LVMH collaborates with leading technology companies, startups, and digital innovators to drive innovation and stay at the forefront of digital transformation. By fostering strategic partnerships and investing in emerging technologies, LVMH gains access to cutting-edge solutions and expertise, accelerating its digital initiatives and enhancing its competitive position in the market. For example, LVMH has partnered with Google Cloud to leverage its data analytics and machine learning capabilities to enhance customer insights and optimize business operations across its brands.
All in all, digital innovation is a cornerstone of LVMH's investment thesis, enabling the company to enhance customer experience, transform retail operations, innovate in product design and development, and make data-driven decisions. By embracing digital transformation and leveraging emerging technologies, LVMH reinforces its position as a leader in the luxury goods industry, driving long-term growth and profitability in an increasingly digital world.
*Do note that all of this is for information only and should not be taken as investment advice. If you should choose to invest in any of the stocks, you do so at your own risk.
*请注意,所有这些仅供参考,不应被视为投资建议。如果您选择投资任何股票,您需要自行承担风险。